Pulse-width modulation (PWM), or pulse-duration modulation (PDM), is a method of controlling the average power delivered by an electrical signal.
Fig: An example of PWM in an idealized inductor driven by a blue line voltage source modulated as a series of sawtooth pulses, resulting in a red line current in the inductor.
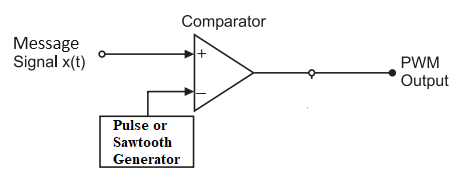
Generating a PWM Signal
The simplest way to generate a PWM signal is the intersection method, which requires only a sawtooth or a triangle waveform (easily generated using a simple oscillator) and a comparator. When the value of the reference signal is more than the modulation waveform, the PWM signal (magenta) is in the high state; otherwise, it is in the low state.
Duty cycle
A low duty cycle equates to low power because the power is off for most of the time; the word duty cycle reflects the ratio of "on" time to the regular interval or "period" of time. The duty cycle is measured in percent, with 100% representing full on. A digital signal has a duty cycle of 50% and looks like a "square" wave when it is on 50% of the time and off the other 50%. A digital signal has a duty cycle of greater than 50% when it spends more time in the on state than the off state. A digital signal has a duty cycle of 50% when it alternates between the on and off states more often than not.
Mathematical Formulation of pulse-width waveform
Pulse-width modulation uses a rectangular pulse wave whose pulse width is modulated resulting in the variation of the average value of the waveform. If we consider a pulse waveform f(t), with period T, low-value ymin, a high-value ymax, and a duty cycle D, the average value of the waveform is given by
Average Value of the Signal and PWM Generation
The average value of the signal is given by:
\[ \bar{y} = \frac{1}{T} \int_0^T f(t) \, dt \] As \(f(t)\) is a pulse wave, its value is \(y_\text{max}\) for \(0 < t < D \cdot T\) and \(y_\text{min}\) for \(D \cdot T < t < T\). The above expression then becomes:
\[ \bar{y} = \frac{1}{T} \int_0^{D \cdot T} y_\text{max} \, dt + \frac{1}{T} \int_{D \cdot T}^T y_\text{min} \, dt \] \[ = \frac{1}{T} \left(D \cdot T \cdot y_\text{max} + T(1 - D) \cdot y_\text{min}\right) \] \[ = D \cdot y_\text{max} + (1 - D) \cdot y_\text{min} \]
From this, the average value of the signal (\(\bar{y}\)) is directly dependent on the duty cycle \(D\).
Further Reading