Stationary and Wide Sense Stationary Process
A stochastic process {…, Xt-1, Xt, Xt+1, Xt+2, …} consisting of random variables indexed by time index t is a time series.
The stochastic behavior of {Xt} is determined by specifying the probability density or mass functions (pdf’s):
p(xt1, xt2, xt3, …, xtm)
for all finite collections of time indexes
{(t1, t2, …, tm), m < ∞}
i.e., all finite-dimensional distributions of {Xt}.
A time series {Xt} is strictly stationary if
p(t1 + τ, t2 + τ, …, tm + τ) = p(t1, t2, …, tm),
∀τ, ∀m, ∀(t1, t2, …, tm).
Where p(t1 + τ, t2 + τ, …, tm + τ) represents the cumulative distribution function of the unconditional (i.e., with no reference to any particular starting value) joint distribution. A process {Xt} is said to be strictly stationary or strict-sense stationary if τ doesn’t affect the function p. Thus, p is not a function of time.
A time series {Xt} is called covariance stationary if
E(Xt) = μ
Var(Xt) = σx2
Cov(Xt, Xt+τ) = γ(τ)
(All constant over time t)
Wide Sense Stationary Process
A random process is called weak-sense stationary or wide-sense stationary (WSS) if its mean function and its correlation function do not change by shifts in time.
μx(t) = μx
Rxx(t1, t2) = Rxx(t1 + α, t2 + α) for every α
Main Properties
- The mean and autocorrelation do not change over time.
- A wide-sense stationary (WSS) process has a constant mean, constant variance, and an autocorrelation function that depends only on the time difference (lag), not the absolute time.
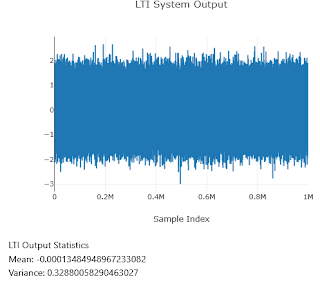
For a WSS input to an LTI system, you are expected to study the output's statistical properties (such as mean, variance, and autocorrelation). You will find that the output signal is also a WSS signal. If your input signal has zero mean and unit variance, then the LTI output will have the same nature as the input signal, but:
- The mean of the output is scaled by the DC gain of the LTI system.
- The variance of the output is scaled by the total power gain of the system.
MATLAB Code to Check the Autocorrelation Property of a WSS Signal Over Time
%The code is developed by SalimWireless.comclc;
clear;
close all;
% Generate a wide-sense stationary (WSS) signal with 0 mean and unit variance
N = 1000; % Length of the signal
X = randn(1, N); % WSS signal
% Define the time indices t1 and t2
t1 = 0; % Time index 1
t2 = 100; % Time index 2
% Initialize autocorrelation value
Rx_val = 0;
% Loop to compute the sum for autocorrelation at (t1, t2)
for n = 1:N
% Ensure indices (n + t1) and (n + t2) are within bounds
if (n + t1 <= N) && (n + t2 <= N)
Rx_val = Rx_val + X(n + t1) * X(n + t2);
else
break; % Stop if indices go out of bounds
end
end
% Normalize by the length of the signal
Rx_val = Rx_val / N;
% Define the time indices t1 and t2
t3 = 100; % Time index 1
t4 = 200; % Time index 2
% Initialize autocorrelation value
Rx_val1 = 0;
% Loop to compute the sum for autocorrelation at (t1, t2)
for n = 1:N
% Ensure indices (n + t1) and (n + t2) are within bounds
if (n + t3 <= N) && (n + t4 <= N)
Rx_val1 = Rx_val1 + X(n + t3) * X(n + t4);
else
break; % Stop if indices go out of bounds
end
end
% Normalize by the length of the signal
Rx_val1 = Rx_val1 / N;
% Display the result
disp(['R_X(', num2str(t2), ') = ', num2str(Rx_val)]);
disp(['R_X(', num2str(t3), ', ', num2str(t4), ') = ', num2str(Rx_val)]);
Output
Copy the MATLAB Code above from here
MATLAB Code for the Output of an ARMA Filter When the Input is a WSS Signal
% Step 1: Get user input for WSS signal parameters
mu = input('Enter the mean of the WSS signal: ');
sigma2 = input('Enter the variance of the WSS signal: ');
N = 1000; % Length of signal
% Generate WSS signal with specified mean and variance
x = sqrt(sigma2) * randn(1, N) + mu;
% Step 2: Define ARMA filter coefficients
b = [1, -0.5]; % MA coefficients
a = [1, -0.8]; % AR coefficients (assumed stable)
% Step 3: Apply ARMA filter using built-in function
y = filter(b, a, x); % y[n] = (b/a) * x[n]
% Step 4: Calculate mean and variance
mean_x = mean(x);
mean_y = mean(y);
var_x = var(x);
var_y = var(y);
% Step 5: Display results
fprintf('Mean of input signal: %.4f\n', mean_x);
fprintf('Mean of output signal: %.4f\n', mean_y);
fprintf('Variance of input signal: %.4f\n', var_x);
fprintf('Variance of output signal: %.4f\n', var_y);
% Step 6: Plot input and output signals
figure;
subplot(2,1,1);
plot(x); title('Input Signal (WSS)'); ylabel('x[n]');
subplot(2,1,2);
plot(y); title('Output Signal (After ARMA Filter)'); ylabel('y[n]');
% Step 7: Autocorrelation comparison
figure;
subplot(2,1,1);
[R_x, lags_x] = xcorr(x - mean_x, 'biased');
plot(lags_x, R_x); title('Autocorrelation of Input x[n]');
xlabel('Lag'); ylabel('R_x');
subplot(2,1,2);
[R_y, lags_y] = xcorr(y - mean_y, 'biased');
plot(lags_y, R_y); title('Autocorrelation of Output y[n]');
xlabel('Lag'); ylabel('R_y');
Output
Enter the variance of the WSS signal: 1
Mean of input signal: -0.0214
Mean of output signal: -0.0545
Variance of input signal: 1.0593
Variance of output signal: 1.3152
Copy the aforementioned MATLAB code from here
Q & A and Summary
1. What is the difference between a random variable and a stochastic process?
Answer:
A random variable is a function that assigns a real number to each outcome of a random experiment, representing a quantity whose value is subject to randomness. Random variables can be either discrete or continuous.
A stochastic process, on the other hand, is a collection of random variables indexed by time, denoted as {Xt | t ∈ T}. Each random variable Xt represents the state of a system at a specific time. It is used to model systems that evolve randomly over time, such as stock prices or weather patterns.
2. What does it mean for a time series to be stationary?
Answer:
A time series is considered stationary if its statistical properties do not change over time. This means that:
- The mean and variance of the series are constant over time.
- The covariance between two time points depends only on the time difference (lag), not on the actual time.
In time series analysis, stationarity is an important assumption for many models, like AR, MA, and ARMA, because these models require the statistical properties of the series to remain stable over time.
3. How do White Noise and Gaussian White Noise differ?
Answer:
White Noise is a type of Wide-Sense Stationary (WSS) process where:
- The mean is zero.
- The variance is constant.
- There is no correlation between values at different times.
If the white noise values also follow a Gaussian distribution (i.e., they are normally distributed), it is referred to as Gaussian White Noise. The key difference is that Gaussian white noise specifically refers to white noise where the random variables have a normal distribution, while white noise could follow any distribution as long as it satisfies the properties mentioned above.
4. What is the Wold Decomposition Theorem and how does it relate to time series models?
Answer:
The Wold Decomposition Theorem states that any Wide-Sense Stationary (WSS) time series can be represented as the sum of two components:
- A predictable deterministic component (like a trend or seasonality).
- A stochastic component, which can be modeled as the output of an LTI (Linear Time-Invariant) system fed by white noise.
This decomposition justifies the use of linear time series models, such as AR, MA, and ARMA, which model the stochastic part of the time series as the output of an LTI system. This allows us to capture the random nature of the series using these models.
5. What is the significance of the z-transform in time series analysis?
Answer:
The z-transform is a mathematical tool used to convert a discrete-time signal (like a time series) into its frequency-domain representation. It is particularly useful for analyzing the properties of time series models, such as ARMA models. The z-transform allows us to represent and manipulate time series models in a more convenient form, especially when working with systems and their stability properties.
- It helps in deriving the transfer function of a system, which relates the input (error terms) and the output (time series).
- It also plays a crucial role in analyzing the stability and invertibility of ARMA models by examining the roots of the AR and MA polynomials in the z-plane.
6. What conditions must be satisfied for an ARMA model to be stable?
Answer:
For an ARMA model to be stable (and hence stationary), the roots of the autoregressive polynomial (Φ(z)) must lie outside the unit circle in the z-plane. This ensures that the time series does not exhibit explosive behavior and remains well-behaved over time. Stability is a key property for ensuring that the statistical properties of the time series do not change over time.
7. How is the transfer function of an ARMA model defined and what does it represent?
Answer:
The transfer function of an ARMA model is defined as the ratio of the moving average polynomial (Θ(z)) to the autoregressive polynomial (Φ(z)) in the z-domain:
H(z) = Θ(z-1) / Φ(z-1)
It describes the relationship between the input (white noise error terms) and the output (time series).
- For a pure AR(p) model, the transfer function is all-pole.
- For a pure MA(q) model, the transfer function is all-zero.
- An ARMA(p,q) model has a pole-zero transfer function.
The transfer function is useful in analyzing the behavior of the system, its stability, and how it filters the white noise to produce the observed time series.
8. Why are AR and MA models important in time series analysis?
Answer:
AR (Autoregressive) and MA (Moving Average) models are essential for capturing the underlying structure of time series data.
- AR models model the current value of the series as a linear combination of its own past values, allowing us to capture patterns such as trends and cycles.
- MA models model the current value as a linear combination of the current and past white noise error terms, which is useful for modeling short-term shocks or noise in the series.
Together, ARMA (Autoregressive Moving Average) models combine both approaches, providing a more powerful tool for modeling and forecasting time series that exhibit both persistence (from AR) and short-term randomness (from MA).
9. How does an LTI system transform a WSS time series?
Answer:
When a Wide-Sense Stationary (WSS) process (like a time series) is passed through a Linear Time-Invariant (LTI) system, the output of the system will also be WSS. This means the statistical properties (mean, variance, covariance) of the time series remain constant over time, even after transformation.
Additionally, if the input WSS process is Gaussian, the output process will also be Gaussian, because the linear transformation preserves the nature of the distribution. This makes LTI systems useful for modeling how time series data evolves over time under various transformations.
10. What practical applications do AR, MA, and ARMA models have in real-world domains?
Answer:
AR, MA, and ARMA models are widely used across many fields, including:
- Economics and finance: Forecasting stock prices, inflation rates, and economic indicators.
- Weather and climate prediction: Modeling temperature, rainfall, and other climate data.
- Signal processing: Analyzing and filtering signals, including audio and communications signals.
- Retail and business sales forecasting: Predicting demand for products based on past sales data.
- Healthcare analytics: Modeling disease spread or patient monitoring data.
These models form the foundation for more complex methods and are critical for both prediction and analysis of time-dependent data.