Determinant using Sarrus rule
Procedure
Choose an n X n matrix
Otherwise-Pop up error – the number of rows and columns should be the same (or matrix dimension mismatched)
Although, Sarrus rule is not applicable for a square matrix which size is greater than 3 X 3, but also we can apply it to obtained 3 X 3 matrix after co-factor expansion of a given matrix.
For a given matrix,
A = $\begin{bmatrix} a11 & a12 & a13 \\ a21 & a22 & a23 \\ a31 & a32 & a33 \end{bmatrix}$
If the number of rows = number of columns = 3, then,
The determinant of this matrix using the Sarrus rule is
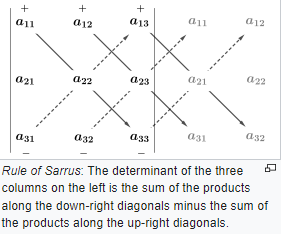
Write out the first two columns of the matrix to the right of the third column, giving five columns in a row.
Then add the products of the diagonals going from top to bottom (solid) and subtract the products of the diagonals going from bottom to top (dashed).
det(A) = a11*a22*a33 + a12*a23*a31 + a13*a21*a32 – a31*a22*a13 – a32*a23*a11 – a33*a21*a12
If the number of rows = number of columns > 3, then
Use cofactor expansion to find the determinant of given matrix
For example,
A = $\begin{bmatrix} a11 & a12 & a13 & a14 \\ a21 & a22 & a23 & a24 \\ a31 & a32 & a33 & a34 \\ a41 & a42 & a43 & a44 \end{bmatrix}$
det(A) = (-1)i+j * a11 * $\left| \begin{matrix} a22 & a23 & a24 \\ a32 & a33 & a34 \\ a42 & a43 & a44 \end{matrix} \right|$ + (-1)i+j * a12 * $\left| \begin{matrix} a21 & a23 & a24 \\ a31 & a33 & a34 \\ a41 & a43 & a44 \end{matrix} \right|$ +
(-1)i+j * a13 * $\left| \begin{matrix} a21 & a22 & a24 \\ a31 & a32 & a34 \\ a41 & a42 & a44 \end{matrix} \right|$ + (-1)i+j * a14 * $\left| \begin{matrix} a21 & a22 & a23 \\ a31 & a32 & a33 \\ a41 & a42 & a43 \end{matrix} \right|$
(In (-1)i+j , ‘i’ denotes the row number and ‘j’ denotes the column number of a matrix element or entry)
Now, you can apply Sarrus rule to find determinant of a matrix which size is 3X3.
Same procedure can be applied for an n X n matrix.
Co-factors and minors of a matrix are already discussed. Please go thru them if you want.
Example
For a 3 X 3 matrix
A = $\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 3 & 5 \\ 2 & 0 & - 1 \\ 4 & - 3 & 1 \end{bmatrix}$ = 1.0.1 + 3.(-1).4 + 5.2.(-3) – 4.0.5 – (-3).(-1).1 – 1.2.3
= 0 -12 -30 – 0 – 3 – 6
= -51
For a 5 X 5 matrix
A = $\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 & 5 \\ 2 & 3 & 4 & 5 & 1 \\ 3 & 4 & 5 & 1 & 2 \\ 4 & 5 & 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 5 & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 \end{bmatrix}$
= (-1)1+1*1* $\left| \begin{matrix} 3 & 4 & 5 & 1 \\ 4 & 5 & 1 & 2 \\ 5 & 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 \end{matrix} \right|$ + (-1)1+2 * 2 * $\left| \begin{matrix} 2 & 4 & 5 & 1 \\ 3 & 5 & 1 & 2 \\ 4 & 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 5 & 2 & 3 & 4 \end{matrix} \right|$ + (-1)1+3 * 3 * $\left| \begin{matrix} 2 & 3 & 5 & 1 \\ 3 & 4 & 1 & 2 \\ 4 & 5 & 2 & 3 \\ 5 & 1 & 3 & 4 \end{matrix} \right|$ +
(-1)1+4 * 4 * $\left| \begin{matrix} 2 & 3 & 4 & 1 \\ 3 & 4 & 5 & 2 \\ 4 & 5 & 1 & 3 \\ 5 & 1 & 2 & 4 \end{matrix} \right|$ + (-1)1+5 * 5 * $\left| \begin{matrix} 2 & 3 & 4 & 5 \\ 3 & 4 & 5 & 1 \\ 4 & 5 & 1 & 2 \\ 5 & 1 & 2 & 3 \end{matrix} \right|$
= 1* $\left| \begin{matrix} 3 & 4 & 5 & 1 \\ 4 & 5 & 1 & 2 \\ 5 & 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 \end{matrix} \right|$ -2 * $\left| \begin{matrix} 2 & 4 & 5 & 1 \\ 3 & 5 & 1 & 2 \\ 4 & 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 5 & 2 & 3 & 4 \end{matrix} \right|$ +3 * $\left| \begin{matrix} 2 & 3 & 5 & 1 \\ 3 & 4 & 1 & 2 \\ 4 & 5 & 2 & 3 \\ 5 & 1 & 3 & 4 \end{matrix} \right|$ -4 * $\left| \begin{matrix} 2 & 3 & 4 & 1 \\ 3 & 4 & 5 & 2 \\ 4 & 5 & 1 & 3 \\ 5 & 1 & 2 & 4 \end{matrix} \right|$ +
5 * $\left| \begin{matrix} 2 & 3 & 4 & 5 \\ 3 & 4 & 5 & 1 \\ 4 & 5 & 1 & 2 \\ 5 & 1 & 2 & 3 \end{matrix} \right|$
Now, $\left| \begin{matrix} 3 & 4 & 5 & 1 \\ 4 & 5 & 1 & 2 \\ 5 & 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 \end{matrix} \right|$ = 3 * $\left| \begin{matrix} 5 & 1 & 2 \\ 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 2 & 3 & 4 \end{matrix} \right|$ -4 * $\left| \begin{matrix} 4 & 1 & 2 \\ 5 & 2 & 3 \\ 1 & 3 & 4 \end{matrix} \right|$ +5 * $\left| \begin{matrix} 4 & 5 & 2 \\ 5 & 1 & 3 \\ 1 & 2 & 4 \end{matrix} \right|$ -1 * $\left| \begin{matrix} 4 & 5 & 1 \\ 5 & 1 & 2 \\ 1 & 2 & 3 \end{matrix} \right|$
= 3 * {(5.2.4 + 1.3.2 + 2.1.3) – (2.2.2 + 3.3.5 + 4.1.1)} -4* {(4.2.4+1.3.1+2.5.3) - (1.2.2 + 3.3.4 + 4.5.1)} + 5* {(4.1.4 + 5.3.1 + 2.5.2) – (1.1.2 + 2.3.4 + 4.5.5)} – 1* {(4.1.3 + 5.2.1 + 1.5.2) – (1.1.1 + 2.2.4 + 3.5.5)}
= -350
(Here in the above we’ve used Sarrus rule to find determinants of 3 X 3 matrices)
Similarly, -2 * $\left| \begin{matrix} 2 & 4 & 5 & 1 \\ 3 & 5 & 1 & 2 \\ 4 & 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 5 & 2 & 3 & 4 \end{matrix} \right|$ = -2*[2*$\left| \begin{matrix} 5 & 1 & 2 \\ 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 2 & 3 & 4 \end{matrix} \right|$ -4*$\left| \begin{matrix} 3 & 1 & 2 \\ 4 & 2 & 3 \\ 5 & 3 & 4 \end{matrix} \right| + 5*\ \left| \begin{matrix} 3 & 5 & 2 \\ 4 & 1 & 3 \\ 5 & 2 & 4 \end{matrix} \right|$
-1* $\left| \begin{matrix} 3 & 5 & 1 \\ 4 & 1 & 2 \\ 5 & 2 & 3 \end{matrix} \right|$]
= -2* [2*{(5.3.4 + 1.3.2 + 2.1.3) – (2.2.2 + 3.3.5 + 4.1.1)} -4* {(3.2.4 + 1.3.5 + 2.4.3) – (5.2.2 + 3.3.3 + 4.4.1)} +5* {(3.1.4 + 5.3.5 + 2.4.2) – (5.1.2 + 2.3.3 + 4.4.5)} -1* {(3.1.3 + 5.2.5 + 1.4.2) – (5.1.1+ 2.2.3 + 3.4.5)}]
(Here also we’ve used Sarrus rule to find determinants of 3 X 3 matrices)
= -2 *[-25] = 50
Similarly, 3 * $\left| \begin{matrix} 2 & 3 & 5 & 1 \\ 3 & 4 & 1 & 2 \\ 4 & 5 & 2 & 3 \\ 5 & 1 & 3 & 4 \end{matrix} \right|$ = 3 * [25] = 75
-4 * $\left| \begin{matrix} 2 & 3 & 4 & 1 \\ 3 & 4 & 5 & 2 \\ 4 & 5 & 1 & 3 \\ 5 & 1 & 2 & 4 \end{matrix} \right|$ = -4 * [-25] = 100
And,
5 * $\left| \begin{matrix} 2 & 3 & 4 & 5 \\ 3 & 4 & 5 & 1 \\ 4 & 5 & 1 & 2 \\ 5 & 1 & 2 & 3 \end{matrix} \right|$ = 5*[400] =2000
So, A = $\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 & 5 \\ 2 & 3 & 4 & 5 & 1 \\ 3 & 4 & 5 & 1 & 2 \\ 4 & 5 & 1 & 2 & 3 \\ 5 & 1 & 2 & 3 & 4 \end{bmatrix}$ = -350 + 50 + 75 +100 + 2000 = 1875